Capstone
Designed a dual interaction mode AI-powered search engine tool to help young professionals facilitate deeper learning.
Designed for
SI 699: Capstone of UX Mastery
Role & Contribution
UX Research
Interaction Design
User Interface Design
Branding
Context
While traditional keyword-based searches and conversational AI tools are effective for finding quick answers or general information, they fall short of facilitating deeper learning or providing structured, comprehensive insights.
How might we design an AI-powered search tool that not only provides structured, deep knowledge but also enables users to explore, organize, and transform that knowledge into meaningful, practical outputs?
Contextual Research:
Current Issues with AI-powered search engines:
“Large language models like ChatGPT are currently not fundamentally trained to speak accurately or stay faithful to some ground truth” (Research & Innovation).
“Content generated by AI tools like ChatGPT, Copilot, and Gemini have been found to provide users with fabricated data that appears authentic” (MIT Sloan Teaching & Learning Technologies).
Primary use of AI-powered search-engines:
69% of AI-powered search engine student users utilize it to search for information (Digital Education Council)
For content creators 58% of them utilize it to generate content ideas (GenAI and the Creator Economy)
1 in 4 Gen Z working adults use AI tools if permitted (Walton Family Foundation)
Design Process
User Interviews, Surveys, Concept Sketches:
25 semi-structured interviews and 18 surveys were conducted. There were three groups we focused on: students, young professionals and content creators. The average age range was 20 - 26 years old, and 85% of them utilized an existing AI-powered search engine tool daily. Concept sketches were made to represent each target user group.
Findings:
Most Valued Features:
70% of survey takers and interview respondents said that the most valued feature of using AI-powered search engine tools was the information summarization feature.
Desire for deeper learning:
55.6% of the respondents noted that AI-powered search tools were inconsistent in accuracy, and 37% responded that, despite AI being faster and more efficient, 59.2% of them still rely on traditional methods for a deeper understanding.
Need for context:
With over half the respondents claiming distrust in accuracy 92.6% of users believed that it was important that AI tools were able to explain how results were relevant and be transparent on the sourcing.
Visual appeal of learning:
A majority of the interview respondents had desired an AI solution that could better facilitate the organization and visualization of information, such as mind-mapping functionalities to make learning more engaging and comprehensive.
Strategy & Solution
Product Strategy:
Our intervention and solution primarily stemmed from the distrust that users have in AI systems. Because the majority of users are already regular users of AI-powered search tools, the concern did not lie in the tool's usage, but rather in its trust and credibility. Furthermore, we wanted to make the tool more accessible; rather than a traditional chat query tool, we wanted to involve the user's wants and needs of facilitating deeper learning through mind-mapping and visual engagement.
Through combining an already existing query functionality, the primary strategy was to evolve the tool into a more credible and engaging workflow tool, allowing user to trust and understand the information they are sourcing and searching.
Solution:
Dual Interaction Mode:
Objective: Offer flexibility in exploring information by allowing users to switch between modes tailored for discovery (Map Mode) and detail-oriented learning (Card Mode).
Justification: Personalized learning paths can improve user engagement and effectiveness. While Card Mode aligns with traditional search-based learning, Map Mode facilitates a systematic, node-based exploration.
Feature Details:
Card View:
A familiar conversation interface with AI, akin to Perplexity.ai, providing answers in card-like containers.
Map View:
Information presented as nodes in a mind map, with expandable layers for related topics, facilitating concept overview and systematic exploration.
Automated Mind Mapping:
Allows users to visualize topic structures in seconds and dive deeper based on interest, addressing structured learning preferences.
Prompt Formatting Mechanism:
Objective: Simplify user interactions with AI to build confidence and reduce cognitive load.
Justification: Studies highlight that knowledgeable users benefit most from time-saving features and that many users experience low confidence in their ability to use AI effectively. By offering guided prompt formatting, users can interact with AI more confidently and efficiently.
Feature Details:
Pre-set Prompts:
Having prompts pre-set for common tasks (e.g., summarizing, brainstorming, categorizing) that allow users to fill in blanks or select keywords.
Example Interface:
Users click on a “Summary” button, activating a pre-filled sentence like “Help me summarize [dropdown]”, with options like “meeting notes,” “research paper,” or “book chapter.”
Design Principle Used:
Recognition rather than recall, which reduces user reliance on memory and encourages more frequent, intuitive AI use.
Source-Verification Mechanism:
Objective: Offer transparency and credibility for source verification methods for users.
Justification: Many GENAI systems have an issue with source transparency, thus leaving users to question the credibility of the information being given. The source verification mechanism will allow them to toggle between windows to see what sources are generating answers.
Feature Details:
Source Demonstration:
Allow the user to view the sources that were utilized in formulating the answer by in-text citation.
Source Placement:
Place the sources utilized at the bottom of the formulated answer by allowing users to click on various links to the actual sources.
Source Page:
Allow users to access a page of citations in order to review the chosen source.
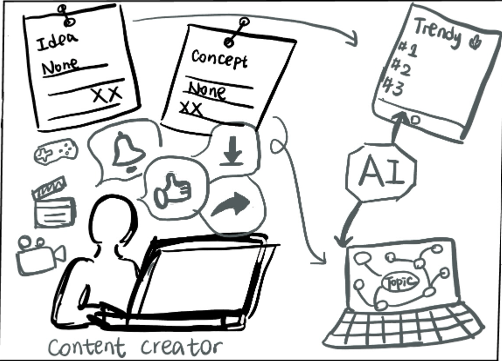
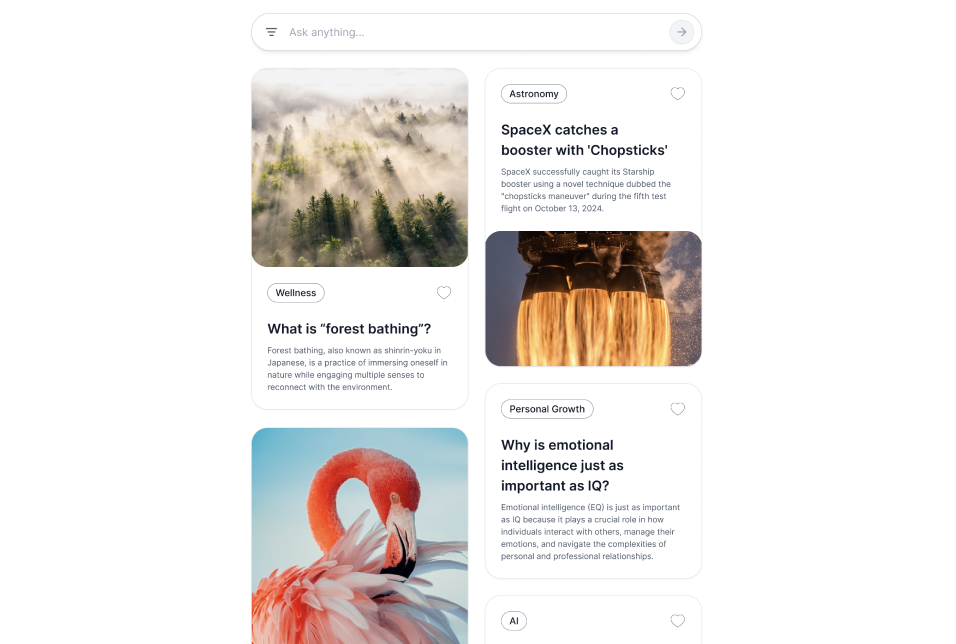
Idea Hub for Trend-Driven Inspiration:
Objective: Offer content creators the opportunity to derive inspiration.
Justification: Given that most content creators use GenAI tools for brainstorming, these features are designed to enhance the creative process by making idea exploration more intuitive, visually engaging, and dynamic.
Feature Details:
Category Navigation:
Each idea card prominently displays its category, enabling users to click on it to explore related ideas. Upon selection, the idea hub dynamically refreshes to showcase all ideas within the same category, enhancing discoverability and contextual exploration.
Enhanced Visual Interest in Images:
Each idea card includes a relevant image alongside the text to make it more visually engaging. These images provide context, spark creativity, and make the browsing experience more captivating and intuitive.
Infinite Flow Interaction:
The idea hub adopts a social media-inspired layout, similar to Twitter, where idea cards are organized for effortless browsing. Users can continuously scroll to uncover a stream of fresh ideas, ensuring an uninterrupted and engaging discovery experience.